Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 10: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SA Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with Hints & Solutions
There is a steady water flow in a horizontal tube in which one part has cross-sectional area and the other part has cross-sectional area . Assume that water is incompressible. If the ratio of the speed in part and the speed in part , i.e., is
A block of wood is floating on oil with half of its volume submerged. If the density of oil , the relative density of wood (relative to water) is
A rubber pipe with a diameter of is connected to a nozzle in diameter. Water flowing through the pipe at a speed of , comes out like a jet through the nozzle. The backward force of the nozzle is about:
Two immiscible liquids, and are kept in a -tube. If the density of liquid is smaller than the density of liquid , then the equilibrium situation is.
An object with uniform density is attached to a spring that is known to stretch linearly with applied force as shown below.
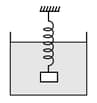
When the spring object system is immersed in a liquid of density as shown in the figure, the spring stretches by an amount When the experiment is repeated in a liquid of density , the spring stretches by an amount, . Neglecting any buoyant force on the spring, the density of the object is
A solid cube and a solid sphere both made of same material are completely submerged in water but to different depths. The sphere and the cube have same surface area. The buoyant force is
A tall tank filled with water has an irregular shape as shown. The wall makes an angle of with the horizontal; the wall is normal to the base . The lengths and are much smaller than the height of water (figure not to scale).

Let and be the pressures exerted by the water on the wall base and the wall respectively. Density of water is and is acceleration due to gravity. Then, approximately

